A) Bond A
B) Bond B
C) Bond C
D) Bond D
E) Bond E
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All of the following contribute to the three-dimensional shape of a protein except
A) temperature.
B) ester linkages.
C) pH.
D) R groups.
E) the peptide backbone.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A macromolecule that is isolated from the bone of dinosaurs and found to have nitrogen-carbon-carbon repeats would be classified as a(n)
A) polysaccharide.
B) oligosaccharide.
C) polypeptide.
D) triglyceride.
E) lipid.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Oil and water do not mix easily because _______ cause the fat molecules of the oil to aggregate together in water.
A) van der Waals forces
B) covalent bonds
C) disulfide bonds
D) ester linkages
E) glycosidic linkages
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Glucose and fructose both have the formula C6H12O6, but the atoms in these two compounds are arranged differently.Glucose and fructose are therefore
A) isomers.
B) polysaccharides.
C) stereosaccharides.
D) pentoses.
E) isotopes.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the figure below. 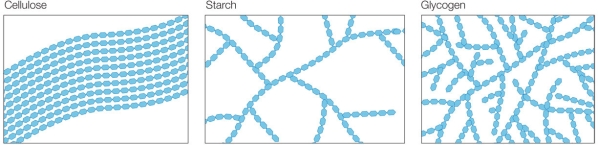 Rank the three structures shown, from lowest to highest density.
Rank the three structures shown, from lowest to highest density.
A) Cellulose, starch, glycogen
B) Starch, cellulose, glycogen
C) Glycogen, starch, cellulose
D) Cellulose, glycogen, starch
E) Starch, glycogen, cellulose
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A molecule with the formula C6H12O6 can be classified as a
A) protein.
B) carbohydrate.
C) lipid.
D) fat.
E) nucleic acid.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A structural isomer for the molecule NaOCH2CH3 would be expected to have how many carbon atoms?
A) One
B) Two
C) Three
D) Five
E) Nine
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the figures below. 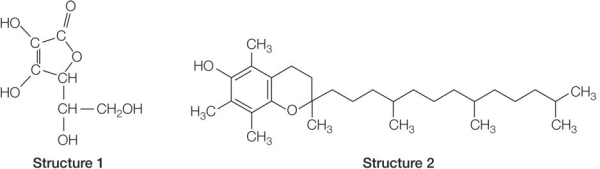 Two vitamin structures are shown.Which would be classified as a lipid, and why?
Two vitamin structures are shown.Which would be classified as a lipid, and why?
A) Structure 1, because of its similarity in structure to cholesterol
B) Structure 1, because most of its structure forms a ring
C) Structure 2, because of its carbon content
D) Structure 2, because of its nonpolar nature
E) Both structures, because of their carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen content
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Hydroxyl groups are polar, and thus a molecule that contains multiple hydroxyl groups will be
A) basic.
B) soluble in water.
C) involved in reactions forming more complex molecules.
D) nonpolar.
E) hydrophobic.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Refer to the figure below. 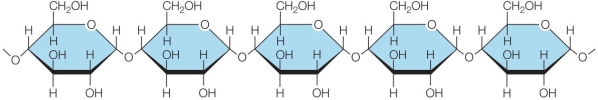 The figure shows a polymeric macromolecule synthesized by cells.The monomer of this polymer is _______.
The figure shows a polymeric macromolecule synthesized by cells.The monomer of this polymer is _______.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the figure below showing a section of a polypeptide chain in a protein. 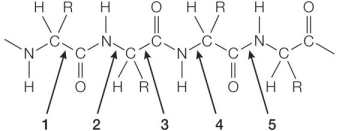 Which bond labeled on the figure undergoes hydrolysis as the chain is broken down to its amino acid building blocks?
Which bond labeled on the figure undergoes hydrolysis as the chain is broken down to its amino acid building blocks?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You are designing an experiment that requires a protein to be exposed to high heat yet remain functional.You find, however, that the protein has lost its function on returning to its normal physiological temperature.You determine that the loss of function is due to an error in refolding of the protein.To remedy this, you could
A) expose the protein to high temperature multiple times.
B) add a chaperone.
C) change the peptide backbone.
D) increase the pH.
E) add mercaptoethanol.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An unknown sample known to contain either triglycerides or phospholipids is placed in water.The sample forms a separate layer on top of the water, with no mixing in the bulk volume of water.What type of lipid does the sample contain, and what structural element is responsible for the sample's behavior in water?
A) Triglycerides, double bonds in fatty acid tails
B) Triglycerides, ester linkages
C) Triglycerides, long-chain hydrocarbon tails
D) Phospholipids, ester linkages
E) Phospholipids, glycerol backbone
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 1 shows a protein enzyme labeled E that catalyzes a chemical reaction involving the substrate molecule labeled C.Figure 2 shows how another molecule, labeled D, binds to a site on the protein that is distinct from the catalytic site. 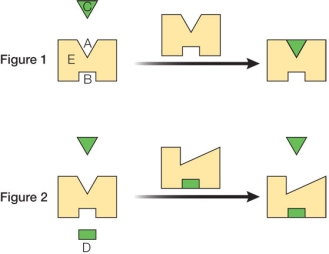 Based on the activities shown, what biological advantage does this protein gain by having the ability to bind molecule D?
Based on the activities shown, what biological advantage does this protein gain by having the ability to bind molecule D?
A) It gains a new chemical reaction that it can catalyze.
B) It gains the ability to bind a broader range of molecules at its catalytic site.
C) It gains a mechanism for preventing the protein from being degraded.
D) It gains a means for turning the biological activity of the protein on and off.
E) It gains the ability to diffuse through cell membranes.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Starch and glycogen are similar in that they both
A) store genetic information.
B) are polymers of amino acids.
C) are composed of fructose monomers.
D) contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
E) denature into a peptide backbone.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Refer to the figure below. 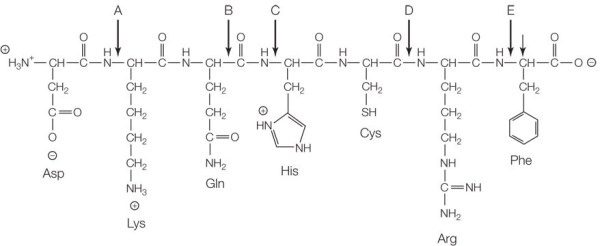 The structure shows an example of a biological polymer called a protein, which is made up of monomers called _______.
The structure shows an example of a biological polymer called a protein, which is made up of monomers called _______.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Olive oil melts at a lower temperature than beef fat because
A) oils contain glycerol, whereas fats do not.
B) fats contain more saturated fatty acids than oils do.
C) fats contain more unsaturated fatty acids than oils do.
D) oils are made by plants, whereas fats are made by animals.
E) olive trees naturally occur in warmer climates than beef cattle do.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Disaccharides are joined together by
A) hydrolysis.
B) glycosidic linkages.
C) peptide bonds.
D) salt bridges.
E) hydrophobic reactions.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A protein is discovered to undergo a reversible phosphorylation reaction in the cell.Scientists do not know whether this phosphorylation has any biological function, but one possibility is that
A) the modification will convert the protein from a cytosolic protein into a membrane-bound protein.
B) the phosphate groups will prevent the protein from denaturing even under high heat or high levels of chemical denaturant.
C) the change will cause the peptide bonds of the protein to weaken and break.
D) the protein will undergo a shape change that will either activate or inhibit its biological activity.
E) the additional phosphate groups will make the protein better able to diffuse through the cell membrane.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 246
Related Exams